Ensuring that your website or pages are indexed by Google is crucial for online visibility. Indexing refers to the process where Google crawls your site and includes it in its search engine database. Without proper indexing, your content won’t appear in search results. Below, we’ll explore how to check if your content is indexed, enable indexing, and address common issues related to Google indexing.
What is Google indexing?
Google indexing is the process by which Google collects, processes, and stores data from your website to display in search results. When a page is indexed, it becomes eligible to appear in search queries related to its content. Google uses bots, commonly referred to as crawlers, to discover new and updated pages. Once the pages are crawled, Google evaluates their content for relevance and ranks them accordingly.
How do you check if a page is indexed?
You can check if a page is indexed using the following methods:
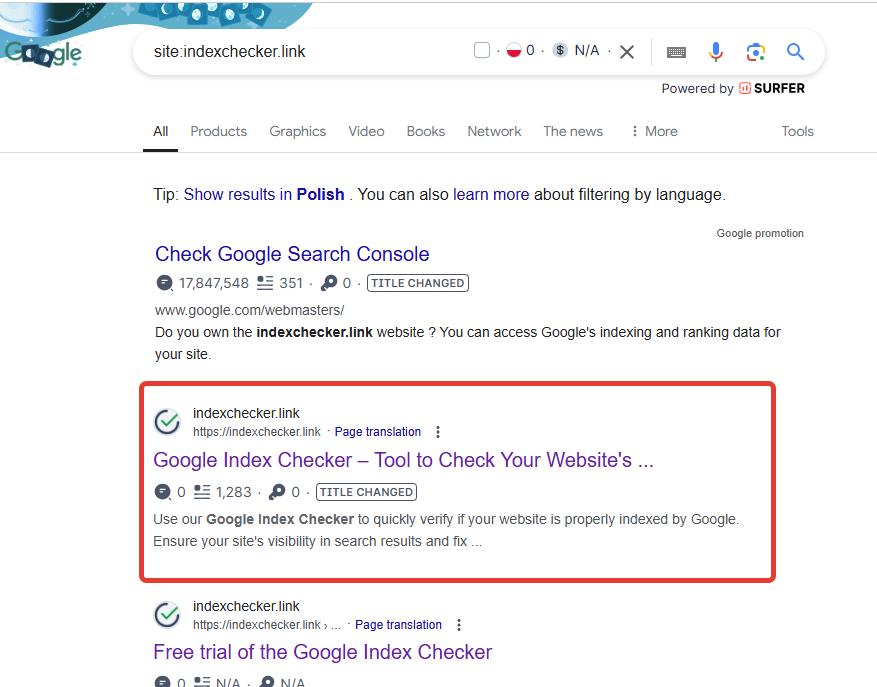
1. Site Search Method
- Type
site:yourdomain.comin Google Search. For example,site:example.com. - If your site appears in the results, it means Google has indexed it.
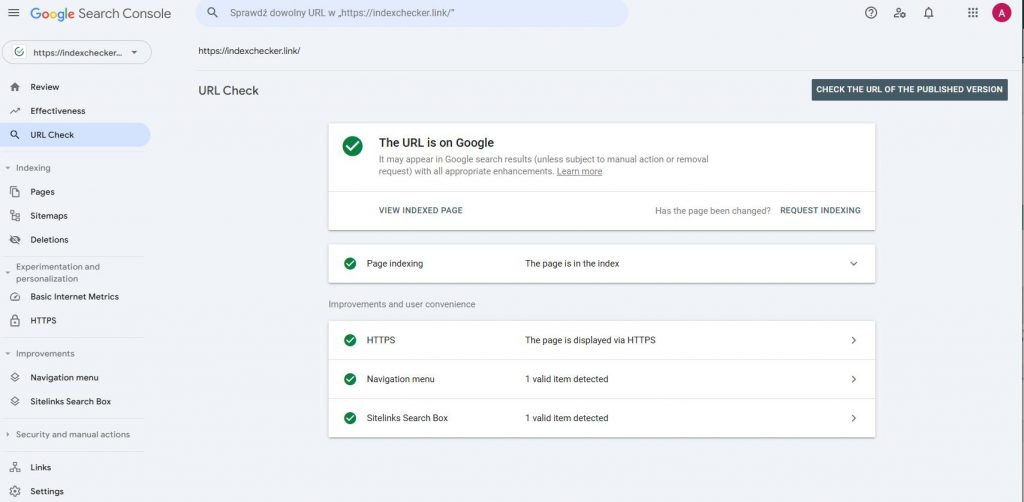
2. Google Search Console
- Log in to Google Search Console.
- Navigate to the URL Inspection Tool.
- Enter your URL to check its status. If indexed, you’ll see a confirmation.
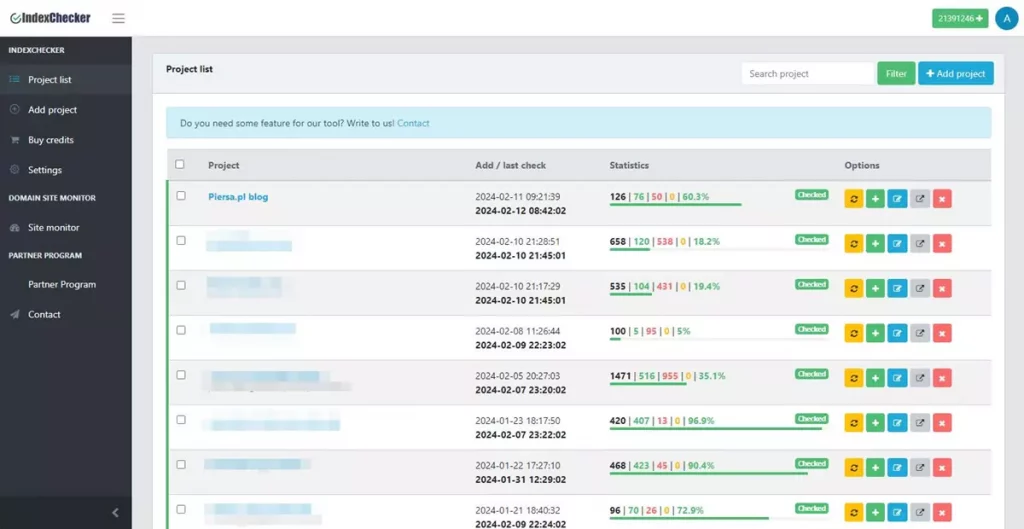
3. Index checker tools
- Use online tools like a google index checker to verify if your page is indexed. These tools simplify the process and can provide additional insights.
How do I enable Google indexing?
If your page isn’t indexed, follow these steps to ensure Google can crawl and index your site:
- Verify Crawlability
- Check your
robots.txtfile to ensure the page isn’t blocked. - Ensure the page has a meta tag like
<meta name="robots" content="index, follow">.
- Check your
- Submit Your Page to Google
- Use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console to request indexing.
- Create and Submit a Sitemap
- A sitemap is a file that lists all the important pages on your website. Submit it through the Sitemaps section in Google Search Console.
- Increase Content Quality
- Ensure your content provides unique value. Avoid duplicate content or thin pages with little information.
- Build Backlinks
- Quality backlinks from other websites can prompt Google to crawl your site faster.
How to check domain index?
Checking a domain’s index status helps assess whether the entire site or specific pages are included in Google’s database.
- Bulk URL Checks: Use tools like index checker google to analyze multiple URLs from a domain at once.
- Search Console Coverage Report: Access the Coverage section in Google Search Console to view a summary of all indexed pages.
- Site-wide Search: Perform a
site:domain.comsearch to check how many pages from your site are indexed.
Common issues affecting indexing
- Blocked by Robots.txt
Ensure critical pages aren’t blocked by yourrobots.txtfile. - Noindex Meta Tag
Remove any<meta name="robots" content="noindex">from pages you want to appear in search. - Duplicate Content
Google might skip indexing pages with duplicate content. Use canonical tags to signal preferred versions. - Thin Content
Pages with little to no value may not be indexed. Add comprehensive, user-focused information to resolve this.
Monitoring indexing status
To monitor your site’s indexing status effectively, leverage tools like Google Search Console or an index checker. Regularly reviewing your site’s performance ensures that newly added or updated pages are indexed promptly, maintaining your site’s search visibility.
Conclusions
Understanding Google indexing is vital for optimizing your website’s performance in search results. By proactively ensuring that your content is crawlable, high-quality, and properly optimized, you can avoid common indexing pitfalls. Tools like index checker google simplify monitoring, ensuring your site remains visible to potential visitors.